Mycotoxins In Feed: Challenges and Mitigation Strategies

What are Mycotoxins?
Mycotoxins are widespread, such as grain growth, harvesting, storage and on-site feeding management. Mycotoxins are very harmful to poultry, swine and Aqua.
Mycotoxins, toxic secondary metabolites produced by fungi, pose significant health risks to poultry and swine. Their presence in feed can lead to a myriad of adverse effects, severely impacting the health and productivity of livestock.
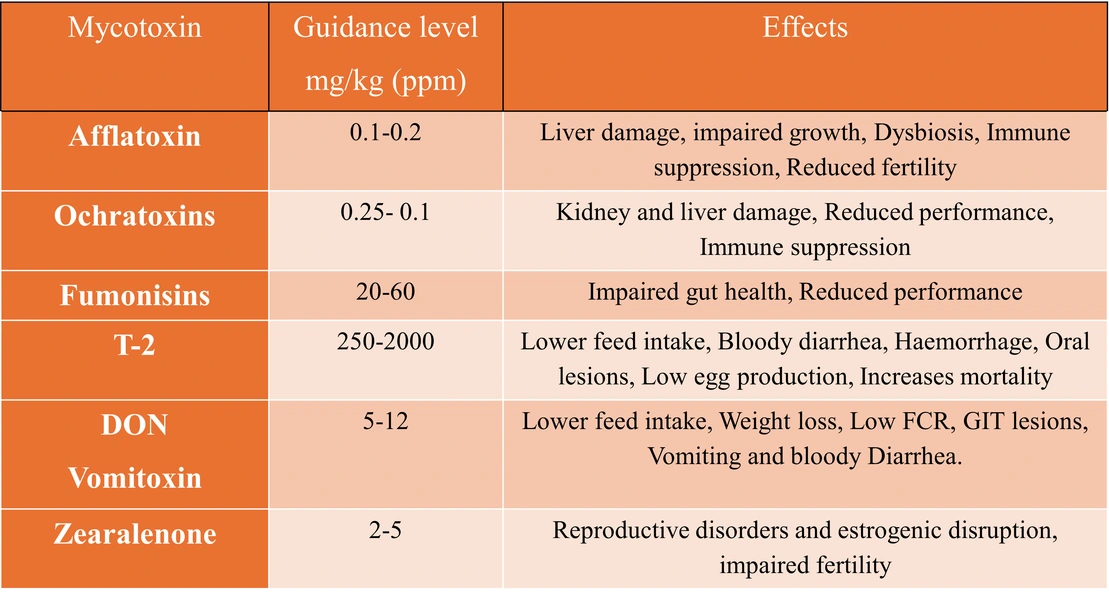
South Asia levels of aflatoxins were highest (70%), followed by ochratoxins (66%), T2 (64%) and FUM (70%). In North America prevalence of ZEN (75%) and DON (73%) were highest.

Consequences of mycotoxin:
- Impaired Growth and Performance: Mycotoxins can cause poor weight gain and feed efficiency in both poultry and swine, leading to economic losses.
- Weak Chicks and Piglets: Exposure to mycotoxins in utero or early in life can result in the birth of weak chicks and piglets with reduced viability and growth potential.
- Intestinal Absorption Disorders: Mycotoxins damage the intestinal lining, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and impaired feed conversion rates. This can cause nutritional deficiencies and stunted growth.
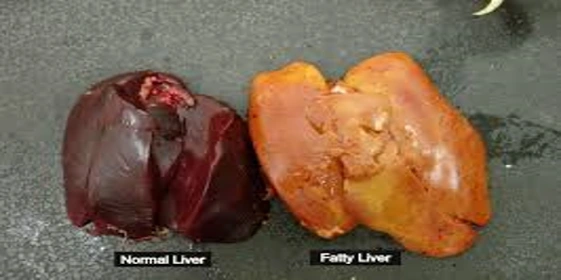
- Liver Damage: Mycotoxins, particularly aflatoxins, cause liver damage, resulting in conditions such as hepatomegaly (enlarged liver) and fatty liver syndrome. This can impair metabolism and overall health.
- Affect Bone Mineralization: Calcium (Ca), Vitamin D, and Phosphorous (P) deficiency leads to inadequate mineralization, weakens the bone, and can cause soft and bent bones or, in the case of layers, cage fatigue – a collapse of the spinal bone- and paralysis.
- Reproductive System Damage: Mycotoxins can affect the reproductive system, leading to issues like reduced fertility, embryonic death, and abnormalities in egg production such as blood spots and sand-shelled eggs in poultry.
- Paleness: Affect red blood cell production by impairing the function of the spleen and inducing haematological alterations. On the other hand, anaemia can be caused by blood loss. Due to affecting coagulation factors, mycotoxins can lead to internal haemorrhages. The gut wall damage, probably due to secondary infections such as coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis, can entail bloody diarrhea in various animal species.

- Immune System Suppression: Mycotoxins compromise the immune system, damaging lymphatic tissues, liver, and spleen. This immunosuppression makes animals more susceptible to bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections.
- Increased Susceptibility to Diseases: With a weakened immune system, poultry and swine become more vulnerable to diseases, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates.
- Respiratory Issues: Mycotoxins can lead to respiratory problems, including increased incidence of respiratory infections and reduced lung function.
- Economic Losses: The direct and indirect effects of mycotoxins lead to significant economic losses due to increased veterinary costs, decreased production efficiency, and loss of livestock.
- Behavioural Changes: Mycotoxins can induce stress and behavioural changes in livestock, including reduced feed intake and altered social interactions.
- Impact on Meat Quality: Mycotoxin contamination can affect the quality of meat, leading to issues like off-flavours, reduced shelf life, and lower market value.

Our Solution
Consumers increasingly demand assurance that animal products are cleaned and safe, leading to a growing preference for natural solutions for mycotoxin mitigation.
Vansh Specialties addresses this need by focusing on natural detoxifiers such as Yeast, enzymes and plant extracts.
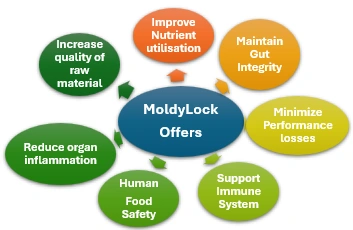
MoldyLock
Organic mycotoxin binder, highly selective mechanism of action against mycotoxin to mitigate their harmful effects that promotes intestinal health and consequently animal performance.
Mode of Action:
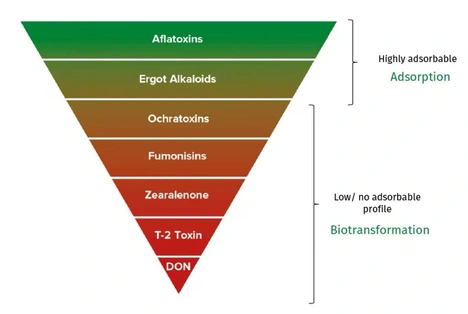
Toxin binders in poultry feed work by altering or adsorbing mycotoxins to reduce their toxicity and enhance excretion. However, clay binders are ineffective against trichothecenes mycotoxins. Biotransformation using microbes and enzymes is more effective, breaking down mycotoxins into non-toxic metabolites.
Microbial methods of mycotoxin directly absorb and metabolise toxins, adsorb/bind them or secrete enzymes that degrade toxins. Additionally, feed additives with plant and algae extracts offer liver protection and counteract immune suppression.
Combining these strategies provides better protection against mycotoxins, especially for multi-mycotoxin contamination in poultry feed.

Key Features of MoldyLock:
- Selectivity for wide range of mycotoxins (DON, ZEN, AFB1, OTA).
- Sparing useful elements eg, macro and Micro minerals, Amino acids.
- Low Effective inclusion rate, High efficacy in mycotoxin binding.
- Rapid and uniform dispersion.
- Heat stability, Stable at wide pH range for effective mycotoxin binding throughout the gut.
- Biodegradable after excretion.