Essential Role of Immunity
Boosters for Broilers and Layers: Supporting Health and Productivity from Early
Age to Maturity
In
swine production, maintaining a robust immune system in both piglets and sows
is essential for health, growth, and reproductive success. Immunity boosters
play a key role in reducing disease risk, promoting growth, and enhancing
productivity across the swine lifecycle.
1. Early-Life Vulnerability in
Piglets:
- Immature Immune Systems: Newborn piglets rely heavily on maternal antibodies from colostrum, as their immune systems are not fully developed. Without adequate early immune support, they are highly susceptible to infections such as neonatal diarrhea caused by E. coli and rotavirus.
- Inconsistent Colostrum Intake: Piglets often vary in their intake of colostrum, leading to disparities in immunity levels within the same litter, which can cause higher mortality and growth variability.
2. Weaning Stress and Immune
Suppression:
- Diet and Environment Change: The transition from sow’s milk to solid feed during weaning is stressful and often leads to “weaning shock,” weakening piglets’ immunity. This stress can increase their susceptibility to gut-related diseases, such as post-weaning diarrhea.
- Environmental and Social Stressors: During weaning, piglets face new environments, mixing with unfamiliar pigs, and competition, which adds stress and suppresses immune function.
3. High-Density Farming and
Pathogen Exposure:
• Disease Transmission: Intensive
pig farming typically involves high-density housing, which facilitates the
rapid spread of pathogens like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome
virus (PRRSV), swine influenza, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.
• Biosecurity Challenges: Maintaining
effective biosecurity in high-density settings can be challenging, increasing
the risk of frequent disease outbreaks that weaken the herd’s overall immune
response.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies:
• Insufficient Immune-Supporting
Nutrients:
Pigs
require balanced diets with adequate levels of vitamins (A, C, E), minerals
(selenium, zinc), amino acids, and antioxidants to support immune health.
Deficiencies in these essential nutrients weaken immunity, making pigs more
prone to disease.
• Variable Feed Quality: Changes
or inconsistencies in feed quality can lead to nutritional gaps, impacting
immune function and overall health.
5. Environmental Stress and
Temperature Variability:
• Temperature Fluctuations: Pigs
are sensitive to temperature changes; extreme heat or cold can stress their
systems and suppress immunity. This is particularly problematic for young
piglets and lactating sows, who are more vulnerable to environmental stress.
• Poor Ventilation and Air Quality: Inadequate
ventilation can lead to high ammonia and dust levels, damaging pigs’
respiratory tracts and making them more susceptible to respiratory diseases.


6. High Pathogen Load in Sows and Vertical Disease Transmission:
- Reproductive Infections: Sows can carry infections that are passed vertically to piglets, such as PRRS and porcine parvovirus, affecting both immune health and overall litter quality.
- Immunity Demands During Lactation: Lactating sows face significant immune demands, and if immunity is not supported, they may experience health issues such as mastitis or metritis, impacting both their health and that of their piglets.
7. Reduced Antibiotic Use and Rising Antimicrobial Resistance:
- Transition to Antibiotic-Free Production: The push toward reduced antibiotic use challenges pig producers to find alternative methods to support immune health and disease resistance.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): AMR is an increasing concern, making it essential to adopt sustainable immunity-boosting strategies, such as probiotics, organic acids, and phytogenic additives, to reduce dependence on antibiotics.

ImmuactWhat is Immuact?Immuact is a premium feed additive formulated to enhance the immunity, health and performance of livestock. Combining the potent benefits of Beta glucans with a proprietary blend of organic acids delivers functional components to support livestock through everyday stress, transitions and disease challenges.
Benefits of Immuact:
- Boosting the Immune System and reduce disease incidence.
- Improves gut health by preventing colonisation of pathogens in gut.
- Reduced the diarrhea.
- Increases the liveability of birds
- Boosting Animal Performance Improves the body weight and FCR
- Increasing Antibody Titers after Vaccination.
- A valuable tool to the producer as an alternative to antibiotics.
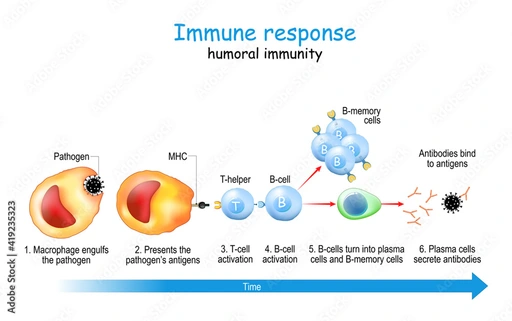
Mode of Action in Animals
1.Immune Modulation: Immuact stimulate the immune system by activating macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer cells, neutralised inflammatory cytokinin, leading to improved pathogen defence, thereby enhancing the animal's ability to fight infections. Nucleotides support rapid cell division and repair, crucial for the immune system. Propionic and butyric acids act as energy sources for intestinal cells and have anti-inflammatory properties, supporting immune health.
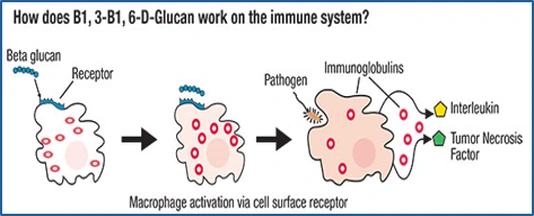
2. Antimicrobial
Effect:
Beta glucans bind to pathogens,
preventing their attachment to the gut lining, altering intestinal microbiota
with competitive exclusion, while organic acids can lower gut pH, inhibit the
growth of pathogenic bacteria in the gut, promoting a healthier microbiome.
3. Growth Promoter: Beta glucan promotes beneficial gut microflora and inhibits pathogens, while organic acids like fumaric and formic acid improve feed conversion by enhancing protein digestion and energy utilization. This combination can lead to better growth rates and feed efficiency.
4. Improved Nutrient Absorption: Glucans and mannan in yeast cell walls can bind to mycotoxins, reducing their absorption in the gut. Organic acids help in detoxifying the gut and maintaining a low pH, preventing the growth of toxin-producing moulds and bacteria. Enhances gut health by promoting SCFA, protect intestinal barrier function, improves tight junction, increase villus height crypt depth, leading to better digestion and nutrient uptake. Citric and lactic acids chelate minerals, enhancing their absorption in the gut. Organic acids reduce pH which activates secretion and activation of gastric and pancreatic enzymes leading better gut health, and better performance.